Angular Pipes: Unleashing the Power of......
Angular Pipes: Unleashing the Power of Data Transformation
Introduction
In the dynamic world of web development, Angular stands as one of the most robust and versatile frameworks for building single-page applications (SPAs). One of the key features that make it a favorite among developers is the use of Angular Pipes. These handy tools allow you to transform and manipulate data in a clean and efficient way, making your web applications more user-friendly and functional.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into Angular Pipes, understanding what they are, how to use them, and exploring some practical examples to solidify our understanding.
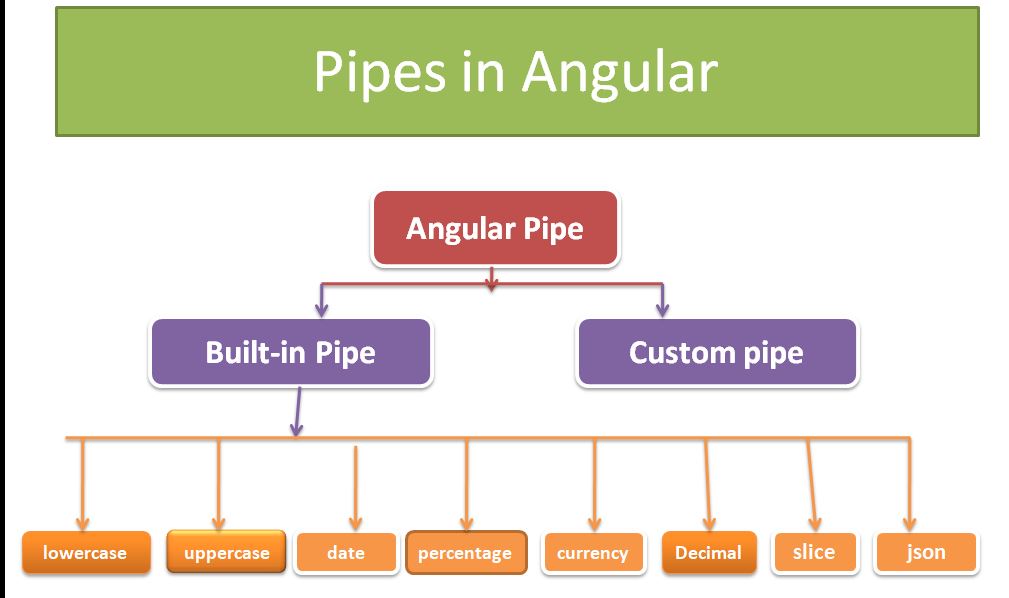
What Are Angular Pipes?
Angular Pipes are a powerful feature that enables you to transform data within your templates. They serve as filters that can format, manipulate, and present data in a more readable and user-friendly manner. Pipes are a crucial aspect of Angular’s data binding mechanism, helping developers seamlessly bridge the gap between the component and the template.
Angular comes with a set of built-in pipes that cater to common data transformations such as date formatting, currency conversion, and uppercase/lowercase transformations. However, you can also create custom pipes to meet your specific application requirements.
Using Angular Pipes
Using Angular Pipes is straightforward, and they can be implemented directly in your HTML templates. The basic syntax for using a pipe is as follows:
{{ data | pipeName: argument1: argument2: ... }}
Here, data represents the input data that you want to transform, pipeName is the name of the pipe you want to use, and argument1, argument2, etc., are optional arguments that you can pass to the pipe for customization.
Practical Examples
Let’s explore some practical examples to see Angular Pipes in action:
1. Uppercase and Lowercase Transformation
Suppose you have a variable message containing a string, and you want to display it in uppercase and lowercase formats. You can achieve this using the uppercase and lowercase pipes.
<p>Uppercase: {{ message | uppercase }}</p>
<p>Lowercase: {{ message | lowercase }}</p>
2. Date Formatting
Angular provides the date pipe to format date objects as per your requirements. For instance, if you have a date variable birthDate, you can format it like this:
<p>Birthdate: {{ birthDate | date:'dd/MM/yyyy' }}</p>
3. Currency Conversion
To display currency values, you can use the currency pipe. Let's say you have a product price stored in the price variable:
<p>Price: {{ price | currency:'USD':'symbol':'1.2-2' }}</p>
This will display the price with the USD symbol and format it with two decimal places.
Creating Custom Pipes
While Angular’s built-in pipes cover many common use cases, you’ll often encounter scenarios where you need to create custom pipes to handle specific data transformations. To create a custom pipe, follow these steps:
- Create a TypeScript file for your pipe, e.g.,
my-custom.pipe.ts. - Define your custom pipe class and implement the
PipeTransforminterface.
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'myCustom'
})
export class MyCustomPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, arg1: any, arg2: any): any {
// Your custom logic here
}
}
- Register your custom pipe in your module by adding it to the
declarationsarray.
import { MyCustomPipe } from './my-custom.pipe';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
// ...
MyCustomPipe
],
// ...
})
export class AppModule { }
- Finally, use your custom pipe in your templates just like the built-in pipes.
<p>Transformed Data: {{ data | myCustom: arg1: arg2 }}</p>