Interceptors In Angular
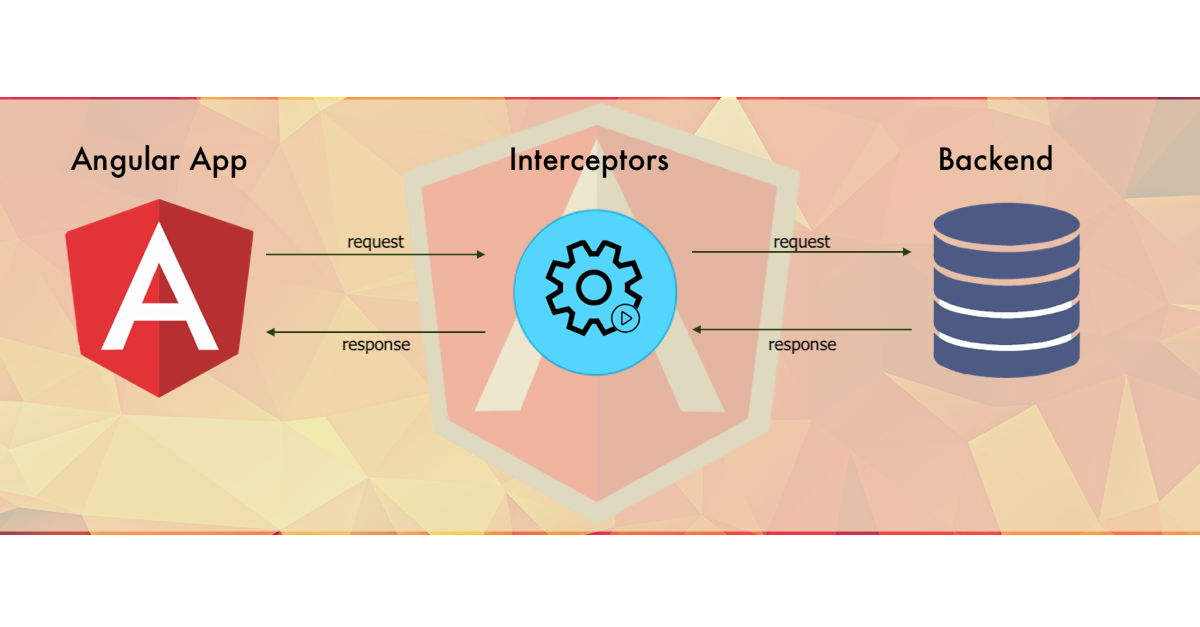
Interceptors In Angular
Interceptors In Angular
Creating interceptors in Angular is a common practice for handling HTTP requests and responses. Interceptors can be used for various purposes such as adding authentication tokens, logging, error handling, etc. Below is a step-by-step guide to create an interceptor in an Angular application.
Step 1: Create the Interceptor
First, generate a new interceptor using the Angular CLI:
sh Copy code ng generate interceptor http
This command will create a new interceptor file, typically named http.interceptor.ts.
Step 2: Implement the Interceptor
Open the generated http.interceptor.ts file and implement the HttpInterceptor interface. Below is an example of an interceptor that adds an authorization token to the headers of each HTTP request:
typescript
Copy code
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpEvent, HttpHandler, HttpInterceptor, HttpRequest } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class HttpInterceptorService implements HttpInterceptor {
intercept(req: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
// Clone the request to add the new header
const authReq = req.clone({
headers: req.headers.set('Authorization', 'Bearer YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN')
});
// Pass on the cloned request instead of the original request
return next.handle(authReq);
}
}
Step 3: Provide the Interceptor
You need to register the interceptor in your application's module. Open your main module file (typically app.module.ts) and provide the interceptor in the providers array:
typescript
Copy code
import { HTTP_INTERCEPTORS } from '@angular/common/http';
import { HttpInterceptorService } from './http.interceptor';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
// your components
],
imports: [
// your modules
],
providers: [
{
provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS,
useClass: HttpInterceptorService,
multi: true
}
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
Step 4: Handling Responses (Optional)
If you want to handle responses or errors, you can do so within the intercept method. For example, to log errors:
typescript
Copy code
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpEvent, HttpHandler, HttpInterceptor, HttpRequest, HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, throwError } from 'rxjs';
import { catchError } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable()
export class HttpInterceptorService implements HttpInterceptor {
intercept(req: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
const authReq = req.clone({
headers: req.headers.set('Authorization', 'Bearer YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN')
});
return next.handle(authReq).pipe(
catchError((error: HttpErrorResponse) => {
// Handle the error here
console.error('Error occurred:', error);
return throwError(error);
})
);
}
}
Summary
- Generate the interceptor using Angular CLI.
- Implement the
HttpInterceptorinterface to handle HTTP requests and responses. - Provide the interceptor in the application's module.
- Optional: Handle responses and errors as needed.