Practical Implementation of Angular Interceptors
Practical Implementation of Angular Interceptors
Let’s start with practical implementation; for that, we need to create a new Angular application using the following command.
ng new angular-interceptor-demo
Now, we are going to create different interceptors one-by-one with the help of angular.
1. Logging Interceptor
In Angular, logging interceptors can be used for audit log purposes. If we want to log different incoming and outgoing requests with request and response objects, we can do so with the help of a logging interceptor.
Step 1
Create a new logging interceptor with the help of the following command.
ng g interceptor logging
This command will create the logging interface with a default implementation. So, modify the same as I have shown below.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import {
HttpEvent,
HttpInterceptor,
HttpHandler,
HttpRequest,
HttpResponse,
} from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, tap } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class LoggingInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
constructor() {}
intercept(
request: HttpRequest<any>,
next: HttpHandler
): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
console.log('Outgoing HTTP request', request);
return next.handle(request).pipe(
tap((event: HttpEvent<any>) => {
console.log('Incoming HTTP response', event);
})
);
}
}
- Here, we import the necessary modules and classes from Angular’s HTTP package.
- The HttpInterceptor interface allows us to create our custom interceptor, and HttpRequest, HttpHandler, and HttpEvent are classes used for handling HTTP requests and responses.
- We also import Observable and Tap from the RxJS library, which is used for handling asynchronous operations.
- We call next.handle(request) to pass the request to the next interceptor in the chain, or the backend server.
- Then, we use the pipe method along with the tap operator to intercept the incoming response.
- The tap operator allows us to execute a side effect (in this case, log the response) without modifying the response itself.
Step 2
Provide an interceptor in the app module:
import { LoggingInterceptor } from './interceptors/logging.interceptor'
providers: [
{
provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: LoggingInterceptor, multi: true
}
]
In the AppModule, we provide the LoggingInterceptor class as an interceptor using the HTTP_INTERCEPTORS token. The multi: true option ensures that the interceptor is appended to the existing array of interceptors rather than replacing them.
When you make an HTTP request, it will get logged with the following request and response:
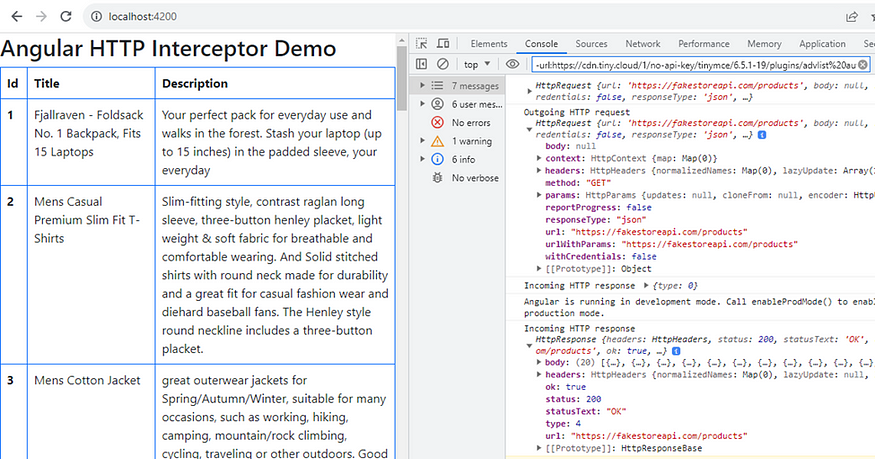
In a real-time scenario, you can log this response in a third-party service as per need and requirement.
2. Adding Headers to Requests
In Angular, we can modify HTTP Requests and add some extra value to the request header with the help of an interceptor.
Step 1
Create a new header interceptor with the help of the following command:
ng g interceptor headers
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import {
HttpRequest,
HttpHandler,
HttpEvent,
HttpInterceptor
} from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class HeadersInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
constructor() {}
intercept(request: HttpRequest<unknown>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<unknown>> {
console.log(request)
const GUID = 'f4179b26-21ac-432c-bcd8-cb4bc6e50981'
const modifiedRequest = request.clone({
setHeaders:{
GUID
}
})
return next.handle(modifiedRequest);
}
}
Here we first hardcode one GUID that we are going to set inside the header. So, first, we need to clone that HTTP request and use the set headers property to set the value in the request header.
Step 2
Provide an interceptor in the app module:
import { HeadersInterceptor } from './interceptors/headers.interceptor'
providers: [
{
provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: HeadersInterceptor, multi: true
}
]
In the AppModule, we provide the HeadersInterceptor class as an interceptor using the HTTP_INTERCEPTORS token. The multi: true option ensures that the interceptor is appended to the existing array of interceptors rather than replacing them.
In a real-time scenario, you can use these header values for further processing, like validating requests, and in many other cases.
3. Error Handling Interceptor
In Angular, The Error interceptor is an HTTP interceptor that allows you to handle HTTP errors globally within your application.
When you make HTTP requests to a server, there might be scenarios where the server responds with an error status code, such as 404 or 500.
Handling these errors in each individual HTTP request can be tedious and repetitive.
The Error Interceptor helps you centralize the error-handling logic and provides a consistent way to manage errors across your application.
Step 1
Create a new error interceptor with the help of the following command.
ng g interceptor error
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import {
HttpRequest,
HttpHandler,
HttpEvent,
HttpInterceptor,
HttpErrorResponse
} from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, catchError, throwError } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class ErrorInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
constructor() {}
intercept(request: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
return next.handle(request).pipe(
catchError((error: HttpErrorResponse) => {
// Handle the error here
console.error('error occurred:', error);
//throw error as per requirement
return throwError(error);
})
);
}
}
- Inside the intercept() method, you can use the catchError operator from RxJS to catch any errors that occur during the HTTP request or response handling.
- This operator allows you to intercept the error, handle it as needed, and optionally re-throw the error to propagate it further up the observable chain.
Step 2
- Provide interceptor in the app module:
import { ErrorInterceptor } from './interceptors/error.interceptor';
providers: [
{
provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: ErrorInterceptor, multi: true
}
]
- In the AppModule, we provide the HeadersInterceptor class as an interceptor using the HTTP_INTERCEPTORS token. The multi: true option ensures that the interceptor is appended to the existing array of interceptors rather than replacing them.
4. Authentication Interceptor
In Angular, an authentication interceptor can be used to add authentication tokens or headers to every outgoing HTTP request. This is helpful when you need to ensure that all API requests are authenticated.
Step 1
Create a new authentication interceptor with the help of the following command.
ng g interceptor auth
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import {
HttpEvent,
HttpInterceptor,
HttpHandler,
HttpRequest,
} from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
//import { AuthService } from './auth.service';
@Injectable()
export class AuthInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
constructor(/*private authService: AuthService*/) {}
intercept(
req: HttpRequest<any>,
next: HttpHandler
): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
const authToken = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpheWRlZXAgUGF0aWwiLCJpYXQiOjE1MTYyMzkwMjJ9.yt3EOXf60R62Mef2oFpbFh2ihkP5qZ4fM8bjVnF8YhA";//his.authService.getToken();
if (authToken) {
// Clone the request and attach the token
const authReq = req.clone({
setHeaders: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${authToken}`
}
});
return next.handle(authReq);
}
// If there is no token, pass the original request
return next.handle(req);
}
}
Here we first hardcode one token that we are going to set inside the header. So, for that first, we need to clone that HTTP request and need to use the set headers property to set the value in the request header.
Step 2
Provide an interceptor in the app module:
import { AuthInterceptor } from './interceptors/auth.interceptor';
providers: [
{
provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: AuthInterceptor, multi: true
}
In the AppModule, we provide the HeadersInterceptor class as an interceptor using the HTTP_INTERCEPTORS token. The multi: true option ensures that the interceptor is appended to the existing array of interceptors rather than replacing them.
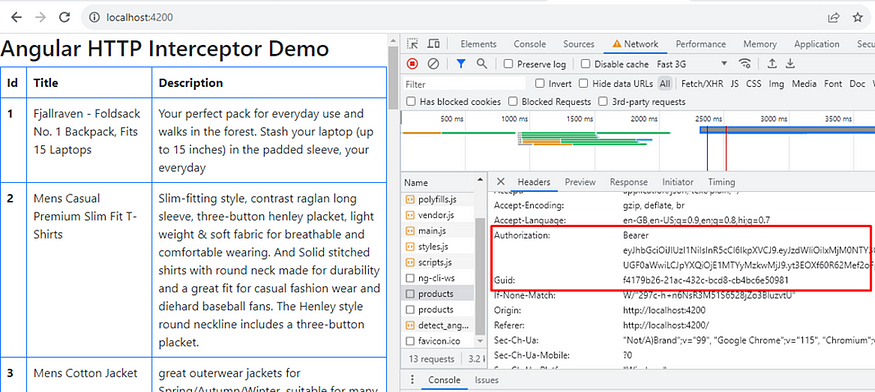
When you make an HTTP request, it will set a token inside the header, as shown below.

As you can see, we set one bearer token that you can use for further processing as per requirement.